LC: Closest Leaf in a Binary Tree
https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-leaf-in-a-binary-tree/
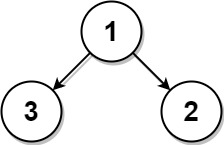
Input: root = [1,3,2], k = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: Either 2 or 3 is the nearest leaf node to the target of 1.Input: root = [1], k = 1
Output: 1
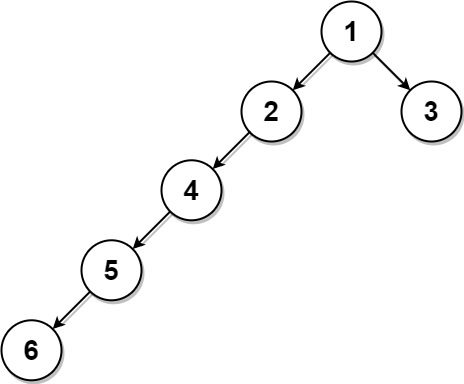
Explanation: The nearest leaf node is the root node itself.Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5,null,6], k = 2
Output: 3
Explanation: The leaf node with value 3 (and not the leaf node with value 6) is nearest to the node with value 2.Last updated